Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we access and utilize data. By leveraging remote servers and on-demand resources, businesses and individuals alike are experiencing a new era of efficiency and scalability. But what exactly are the applications of cloud computing, and how are these technologies impacting various industries?
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Understanding Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of on-demand computing services – including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, intelligence – over the internet. Instead of managing physical hardware and software infrastructure, users access these resources remotely through a cloud provider’s platform. This model offers a plethora of benefits, making it a cornerstore of modern IT strategies.
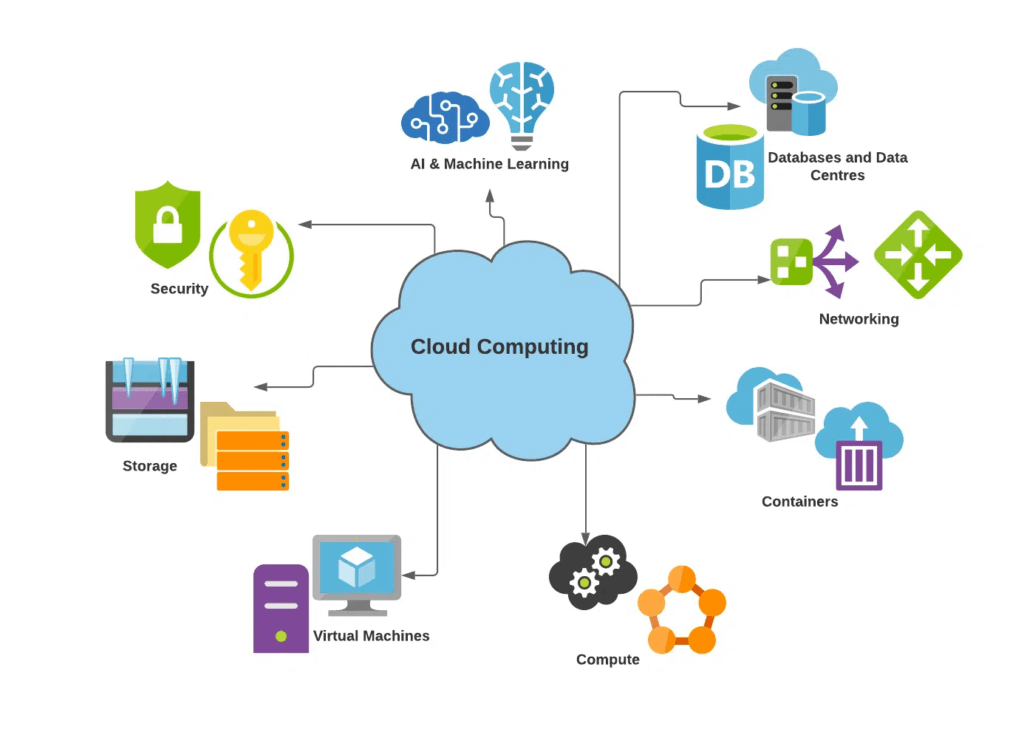
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing
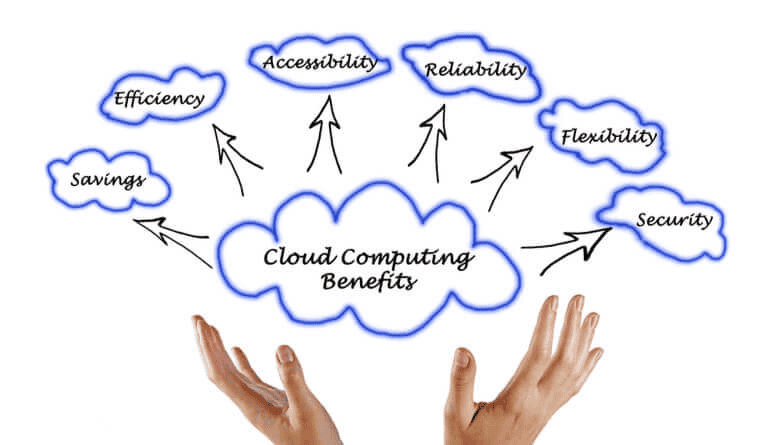
The advantages of cloud computing are numerous and far-reaching. Here are some of the most significant benefits:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud computing eliminates the upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure. Businesses only pay for the resources they use, leading to significant cost savings, especially for startups and small businesses.
- Scalability: Cloud resources can be easily scaled up or down based on demand. This allows businesses to adapt to fluctuating workloads efficiently, such as seasonal peaks or unexpected surges in traffic.
- Increased Agility: Cloud-based solutions enable faster deployment of applications and services, allowing businesses to respond to market changes quickly and seize opportunities for growth.
- Improved Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, offering a more robust security posture compared to on-premises solutions. They employ a team of cybersecurity experts who are constantly monitoring for threats and implementing the latest security patches.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Cloud platforms facilitate seamless collaboration and data sharing, especially for geographically dispersed teams. Team members can access and work on the same documents simultaneously, improving communication and project efficiency.
- Automatic Updates: Cloud providers handle software updates and maintenance, eliminating the need for manual intervention and reducing downtime. This ensures that businesses are always using the latest versions of software, which improves security and functionality.
- Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based data backups and disaster recovery solutions ensure business continuity in case of unforeseen events like natural disasters or power outages. Data is replicated across geographically diverse locations, minimizing downtime and data loss.
These benefits make cloud computing an attractive proposition for businesses of all sizes and across various industries.
Now let us talk about the applications of cloud computing in Business and industry sector
Cloud Computing in Business and Industry
Cloud computing has permeated nearly every sector, transforming the way businesses operate and deliver value. Here are some specific cloud computing use cases across different industries:
Cloud-Based Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
Cloud-based CRM systems provide businesses with a centralized platform to manage customer interactions, track leads, and nurture relationships. These solutions are accessible from anywhere, anytime, allowing sales teams to collaborate effectively and improve customer satisfaction. Additionally, advanced analytics capabilities offered by cloud-based CRMs provide valuable insights into customer behavior, enabling businesses to personalize marketing campaigns and improve customer retention.
Going beyond the basics:
Beyond the core functionalities, some cloud-based CRM systems offer features like:
- Social media integration: Track and respond to customer inquiries on social media platforms directly within the CRM.
- Marketing automation: Schedule and automate marketing campaigns based on customer data and behavior.
- Mobile access: Access CRM data and manage customer interactions from mobile devices.
These advanced features empower businesses to build stronger relationships with their customers and drive sales growth.
Cloud Computing in Healthcare
The healthcare industry is increasingly reliant on cloud technology for a variety of purposes:
- Secure Patient Data Storage: Cloud platforms offer secure and HIPAA-compliant storage for sensitive patient data, such as medical records and imaging results. This facilitates easy access for authorized healthcare professionals while maintaining patient privacy.
- Medical Imaging Analysis: Cloud computing provides the processing power required for complex medical image analysis tasks, such as analyzing X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. This allows for faster diagnoses and more effective treatment plans.
- Remote Collaboration: Cloud-based solutions enable healthcare professionals from different locations to collaborate on patient cases securely. This is particularly beneficial for specialists and consultations across different facilities.
- Telehealth Services: Cloud computing facilitates the delivery of telehealth services, allowing patients to access medical consultations remotely via video conferencing. This improves access to healthcare for patients in rural areas or those with mobility limitations.
Cloud Solutions for Financial Services
Financial institutions leverage cloud computing for several critical functions:
- Secure Data Storage: Cloud providers offer robust security measures to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive financial data, such as customer accounts and transaction records.
- Fraud Detection and Risk Management: Cloud-based analytics tools can analyze vast amounts of financial data in real-time to identify potential fraudulent activity and manage risk exposure. This helps financial institutions protect their customers and assets.
- Personalized Financial Products: Cloud computing allows financial institutions to develop and offer personalized financial products and services based on individual customer needs and financial data.
- Enhanced Customer Experiences: Cloud-based solutions enable financial institutions to provide seamless online and mobile banking experiences for their customers. This includes features like online account management, mobile payments, and real-time transaction notifications.
Cloud Computing in Education
Educational institutions are utilizing cloud solutions for various educational advancements:
- Online Learning Platforms: Cloud-based learning platforms provide a virtual environment for delivering educational content, conducting online courses, and facilitating student-teacher interaction. This enables flexible learning opportunities for students who cannot attend traditional classroom settings.
- Secure Student Data Management: Cloud computing offers secure storage and management of student data, such as grades, transcripts, and attendance records. This ensures data accessibility for authorized personnel while maintaining student privacy.
- Collaboration Tools: Cloud-based collaboration tools enable students and educators to work together on projects, share documents, and communicate effectively, fostering a more interactive learning environment.
- Personalized Learning Experiences: Cloud platforms can be used to analyze student data and personalize learning experiences. This allows educators to tailor their teaching methods to individual student needs and improve learning outcomes.
By leveraging cloud computing, educational institutions can create a more engaging and accessible learning environment for students of all backgrounds.
This section provides a brief overview of cloud computing applications in various industries. As cloud technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative use cases to emerge across different sectors.
Now let us learn about the applications of cloud computing in government and public sector.
Cloud Computing in Government and Public Sector
While traditional government IT infrastructure relied on on-premises data centers, cloud computing offers a compelling alternative. Here’s a deeper dive into how cloud technology is enhancing government services:
- Increased Transparency and Citizen Engagement: Cloud-based platforms can be used to publish government data and reports online, making them easily accessible to citizens. This fosters transparency and encourages public participation in government decision-making processes.
- Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings: Cloud computing allows government agencies to scale resources up or down based on demand, eliminating the need for expensive upfront investments in hardware and software. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Communication: Cloud-based collaboration tools enable government employees from different departments and agencies to work together seamlessly on projects and share information securely. This streamlines communication and fosters better coordination across various government functions.
- Streamlined Service Delivery: Cloud solutions can be used to deliver a wide range of government services online, such as permit applications, tax filing, and social welfare program enrollment. This improves convenience and accessibility for citizens, allowing them to interact with the government on their own terms.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud-based data backups and disaster recovery solutions ensure that critical government services remain operational in case of unforeseen events like natural disasters or cyberattacks. This minimizes downtime and disruptions to essential public services.
Examples of Cloud Computing in Government:
- E-governance Initiatives: Many governments are launching e-governance initiatives to provide online access to government services. These initiatives leverage cloud computing to ensure scalability, security, and efficient service delivery.
- Public Safety Applications: Cloud-based solutions can be used to analyze crime data, track suspicious activity, and improve emergency response times.
- Social Welfare Programs: Cloud computing can be used to manage social welfare programs more effectively, streamlining eligibility verification and benefit disbursement processes.
Emerging Trends and Future Applications of cloud computing
The future of cloud computing is brimming with exciting possibilities. Here’s a closer look at some key trends shaping the landscape:
Internet of Things (IoT) and Cloud Computing
The integration of IoT devices with cloud computing is transforming industries like manufacturing, logistics, and smart cities. Sensor data collected from connected devices is stored, processed, and analyzed in the cloud, enabling real-time insights, predictive maintenance, and intelligent automation. This allows businesses to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge.
For instance:
- Manufacturing companies can use cloud-based IoT solutions to monitor the performance of equipment on the factory floor, identify potential issues before they occur, and schedule preventive maintenance.
- Logistics companies can track the location and condition of goods in real-time, optimizing delivery routes and ensuring product quality.
Applications of Cloud Computing in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The vast computing power and storage capacity of the cloud are essential for training and deploying AI and ML models. Cloud platforms provide the infrastructure for processing massive datasets and building intelligent applications that can learn and adapt over time. This is driving advancements in various fields such as:
- Personalized medicine: Cloud-based AI can analyze patient data to develop personalized treatment plans and improve healthcare outcomes.
- Financial fraud detection: Machine learning algorithms can analyze financial transactions in real-time to identify and prevent fraudulent activity.
- Autonomous vehicles: Cloud computing plays a critical role in developing and deploying self-driving cars by providing the infrastructure for processing sensor data and making real-time decisions.
Impact of Cloud Computing on Smart Cities
Cloud computing is a cornerstone of smart city initiatives. It facilitates data collection from sensors across the city infrastructure, enabling real-time traffic management, optimized energy consumption, and enhanced public safety. Cloud-based solutions also empower citizens to interact with city services through mobile applications, improving their overall quality of life.
Examples of Cloud Computing in Smart Cities:
- Traffic management systems: Cloud-based solutions can be used to analyze traffic data in real-time and adjust traffic lights dynamically to reduce congestion.
- Energy management systems: Cloud computing can help cities optimize energy consumption by monitoring energy use in buildings and public spaces.
- Waste management systems: Cloud-based solutions can be used to track waste collection routes and optimize waste disposal processes.
By leveraging cloud technology, cities can become more sustainable, efficient, and livable for their residents.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an indispensable tool for businesses, organizations, and governments of all sizes. Its versatility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness make it a driving force behind innovation and transformation across numerous industries. As cloud technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more exciting applications that will shape the future of how we work, learn, and interact with the world around us. By embracing cloud computing, organizations can unlock a wealth of opportunities to improve efficiency, enhance collaboration, and achieve their strategic goals.